Last Week in Collapse: May 12-18, 2024
Record temperatures, record migration, record emissions, record displacement, record PFAS……start building an ark.
Last Week in Collapse: May 12-18, 2024
This is Last Week in Collapse, a weekly newsletter compiling some of the most important, timely, useful, soul-crushing, ironic, stunning, exhausting, or otherwise must-see/can’t-look-away moments in Collapse.
This is the 125th newsletter! This one has a ton of images. You can find the May 5-11 edition here if you missed it last week. Thank you for subscribing to the Substack.
——————————
Flash flooding in northern Afghanistan killed 300+ people and destroyed 1,000+ homes. Hundreds of thousands of others have been affected. Last month, similar floods in the region killed 70+. Four died in Texas storms last week as well.
Venezuela is suffering from record wildfires, which so far this year have burned about 5M acres—almost the size of Sardinia. Some experts think indigenous people started the blaze as an attempt at forest clearance, which quickly got out of hand. “Institutional failures” compounded the disaster when the ailing government responded with an inadequate number of poorly equipped firefighters. Another study from last week examined the impact of wildfires on soil health.
Flooding and “cold lava” killed 50+ in Indonesia, injuring dozens and displacing several thousand. Cold lava is a mixture of water and rocks tumbling down the side of a volcano. Meanwhile, an actual volcano erupted in Indonesia, sending smoke & ash 5000m high; further eruptions are possible soon.
The Swiss Re Institute published a 37-page report last week about natural disasters in 2023—and how much damage, in USD, they caused. The largest catastrophe was the February 7.8 earthquake in Türkiye & Syria, which killed 59,000+ people and caused $163B+ in damage. The report is full of interesting graphics & data about natural disasters.
“Last year, economic losses from natural catastrophes reached USD 280 billion, meaning that 62% of the global losses were uninsured….the insured losses surpassed USD 100 billion for the fourth consecutive year….annual insured losses will grow by 5–7% over the long term…today’s insured losses could double in 10 years….There were 142 insured-loss inducing catastrophes in 2023, a new record. Most were of medium severity, which we define as events resulting in losses of USD 1–5 billion….Over the last 30 years, we estimate that natural catastrophe insured losses have grown by 3 percentage points more annually than the global economy (in inflation adjusted terms)...”
Flooding and heat waves are impacting Brazil’s oranges, responsible for about 70% of the world’s supply. One food analysts declared that the “era of cheap food is over”—in the UK, at least. That may be one reason why UK residents took record food bank packages last year. Madagascar is struggling to adapt to a future with far less rainfall.
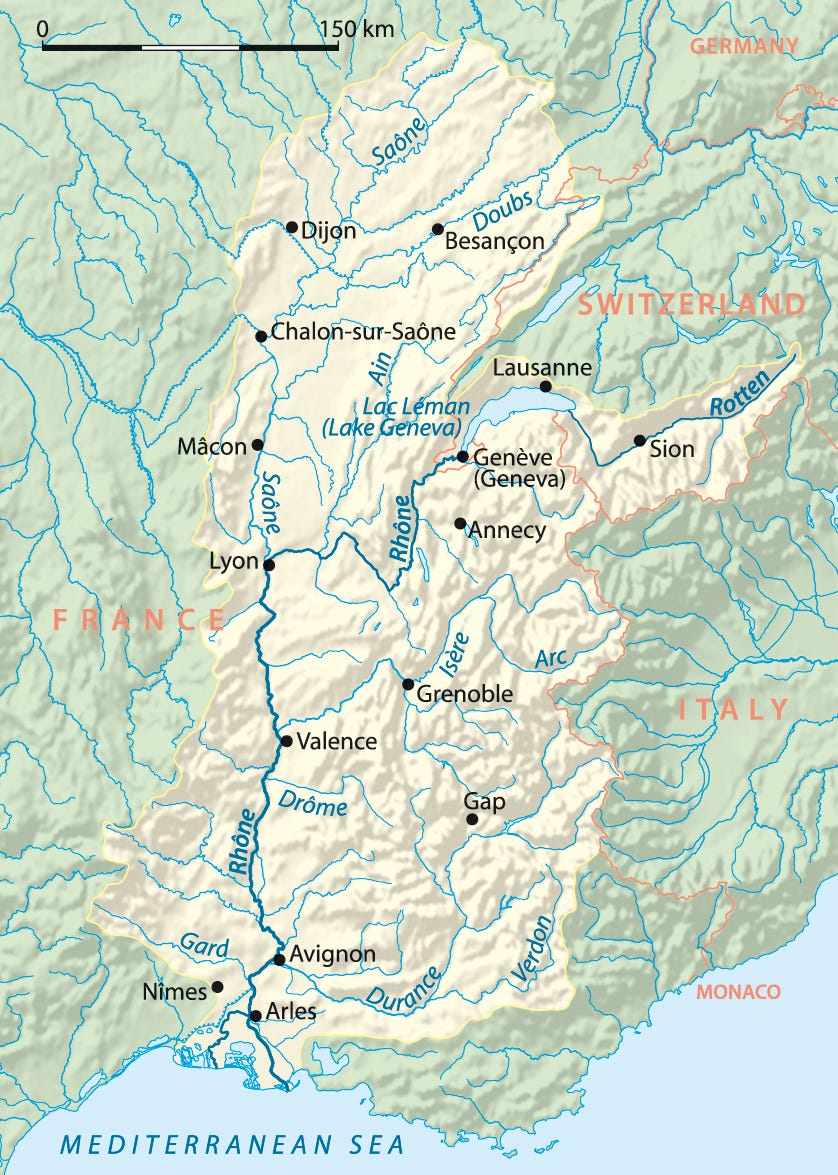
France is growing more concerned about a dam on Lake Geneva, controlled exclusively by Switzerland. The Rhône River, which begins in Switzerland and flows south through France, is shrinking in summers as climate change melts Switzerland’s remaining glaciers.
The Tonlé San River has been dammed in Vietnam, lowering the level in Cambodia and sometimes drying the river downstream entirely. Meanwhile, China’s lychee harvest is getting blasted by rain, impacting the world’s largest source of lychee. And, once again, Saudi Arabia is suffering flooding in its inland regions. 7 dead in historic flooding in Iran.
The eminent climate scientist James Hansen posted that, since “human-made aerosols and their cooling effect are in decline,” the cooling effect of La Niña will be counterbalanced by these rising temperatures. He also identifies a “large anomaly of increased absorbed solar radiation at midlatitudes in the Northern Hemisphere” responsible for rising temperatures there. CO2 levels are rising faster today than they have at any point in the previous 50,000 years…and a study of millennia-old trees determined last summer was the hottest worldwide in 2,000+ years…
Record nighttime May temperatures were tied in the Philippines and Vietnam. A couple Indonesian cities broke records for May temperatures. And a number of southern African states saw more records drop. And Toronto saw a record tied for the number of days reaching 14 °C (57 °F). A heat wave has returned to Bangladesh. Flooding in Cali (pop: 2.9M), Colombia.
The University of Washington was ordered to stop a geoengineering project that scientists sere conducting from the deck of a decommissioned aircraft carrier. The experiment ejected aerosolized saltwater in an attempt to reflect solar radiation. A comparative study in Nature Communications of a number of carbon pricing found that, yes, carbon pricing does work to reduce the total CO2 emitted.
It’s that time of the year again. Wildfires in Canada grow, some of which are moving towards the tar sands—forcing thousands to evacuate. 39 of the total nation’s blazes are “out of control,” resulting in air quality alerts in the United States. Meanwhile, across the Caribbean, water shortages have become the new normal, and residents (and tourists) are finding their old consumption habits hard to change. St. Lucia has declared a water emergency. In Myanmar, water shortages worsen, particularly as related to the spiraling conflict.
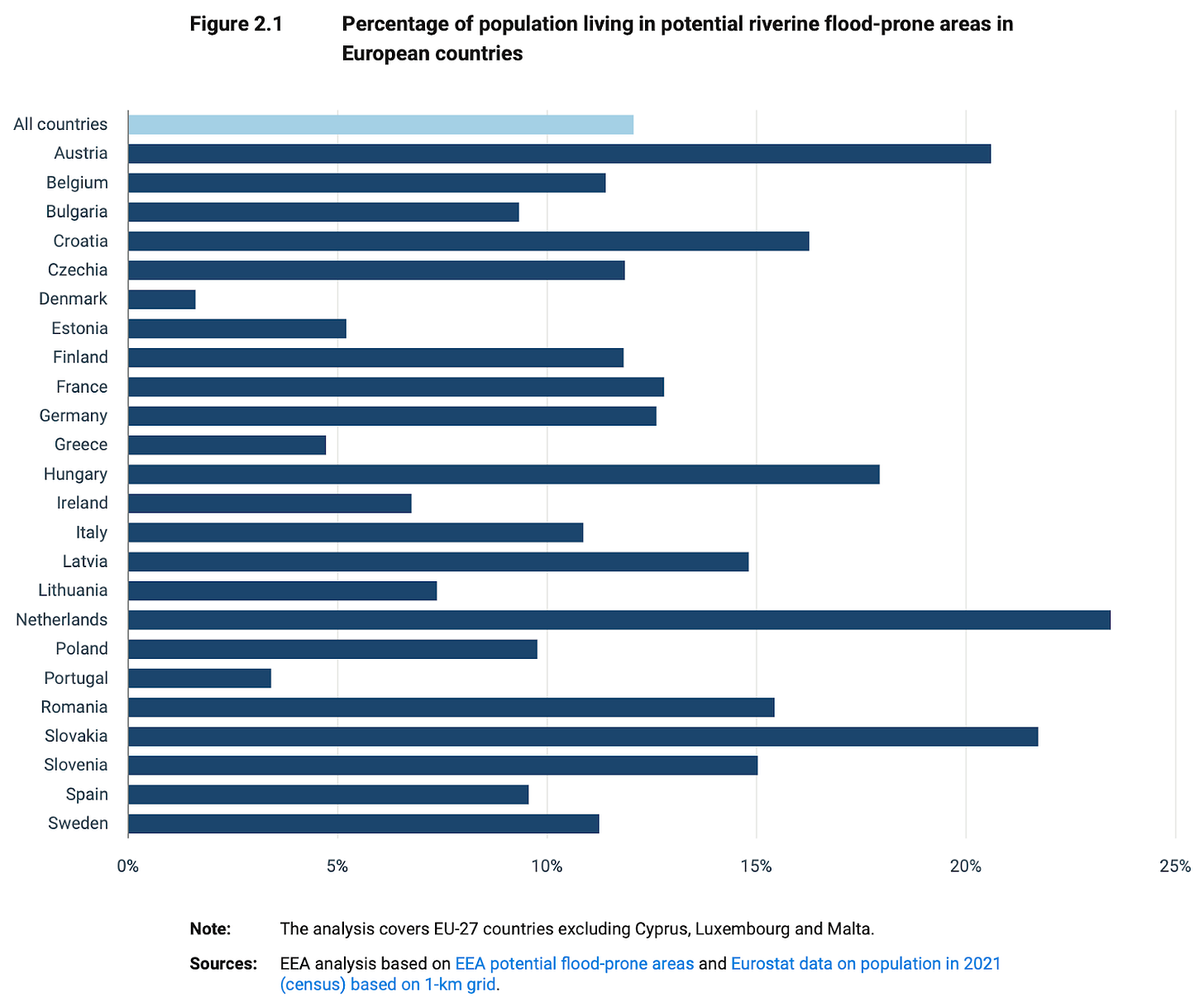
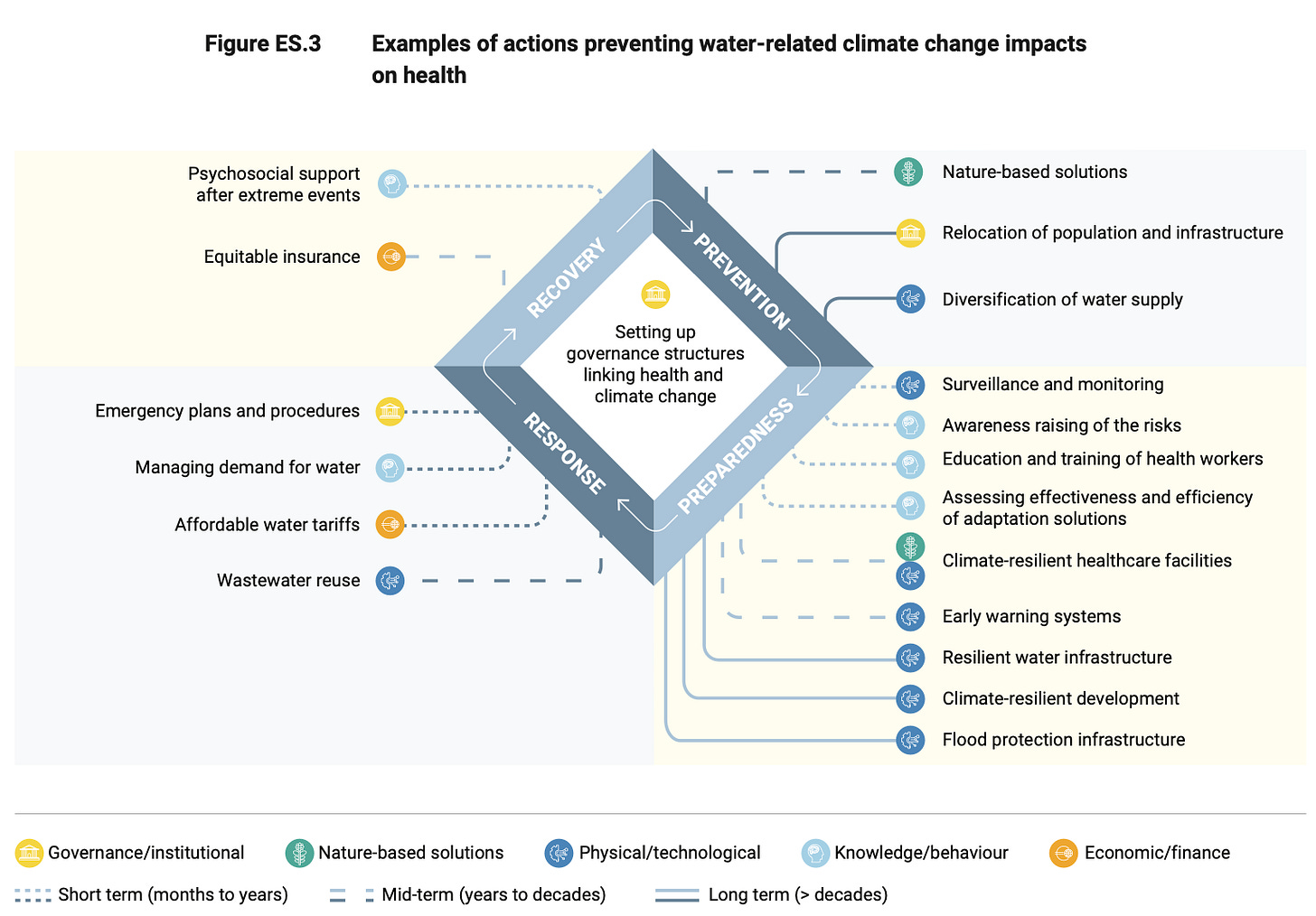
At least ⅛ of Europeans live in a place at risk of extreme flooding—so says a 175-page report from the European Environment Agency posted on Wednesday. The number of people living in flood-risk coastal areas in the EU & UK is expected to jump 24% by 2050. The graphics-packed report also considers how flooding will impact healthcare facilities, mental health, wastewater treatment plants, the spread of disease, cyanobacteria, permafrost thaw, and much else.
“Europe has seen devastating floods following record rainfall, droughts of magnitudes not experienced in hundreds of years, continuing sea level rise, and increasing lake and sea temperatures….permanent water stress already affects 30% of people in southern Europe….since 2018, more than half of Europe has been impacted by extreme drought conditions….Climate change is expected to increase mercury bioaccumulation in the marine food chain due to rising ocean temperatures, ocean acidification and permafrost thawing….Depression, anxiety and PTSD may persist for years after a flooding event….Under the changing climate, northern Europe is becoming wetter in general, but drier in summer. Southern Europe is becoming drier, especially in winter. For central-eastern and western Europe, the trend is less clear…” -selections from the report
Milan suffered flooding last week, the worst May flooding in 170 years. Early spring in the UK has disrupted migratory bird species and their usual patterns.
A 74-page working paper which is not yet peer-reviewed claims that earlier estimates for how much GDP would be impacted by another 1 °C temperature rise is way less than it would be in actuality. The paper claims the real cost (in USD) is about 6x greater. They claim “global temperature has much more pronounced impacts on economic activity than local temperature” and that extreme weather is mostly behind the projected decline in productivity.
——————————
Epidemiologists are worried about how climate change in Africa may extend the life of disease-bearers like ticks and mosquitoes. Other epidemiologists are worried about how cattle may become a permanent reservoir for H5N1. Growing traces of bird flu have been found in wastewater testing in the U.S., but investigators think it may be runoff from infected dairy farms.
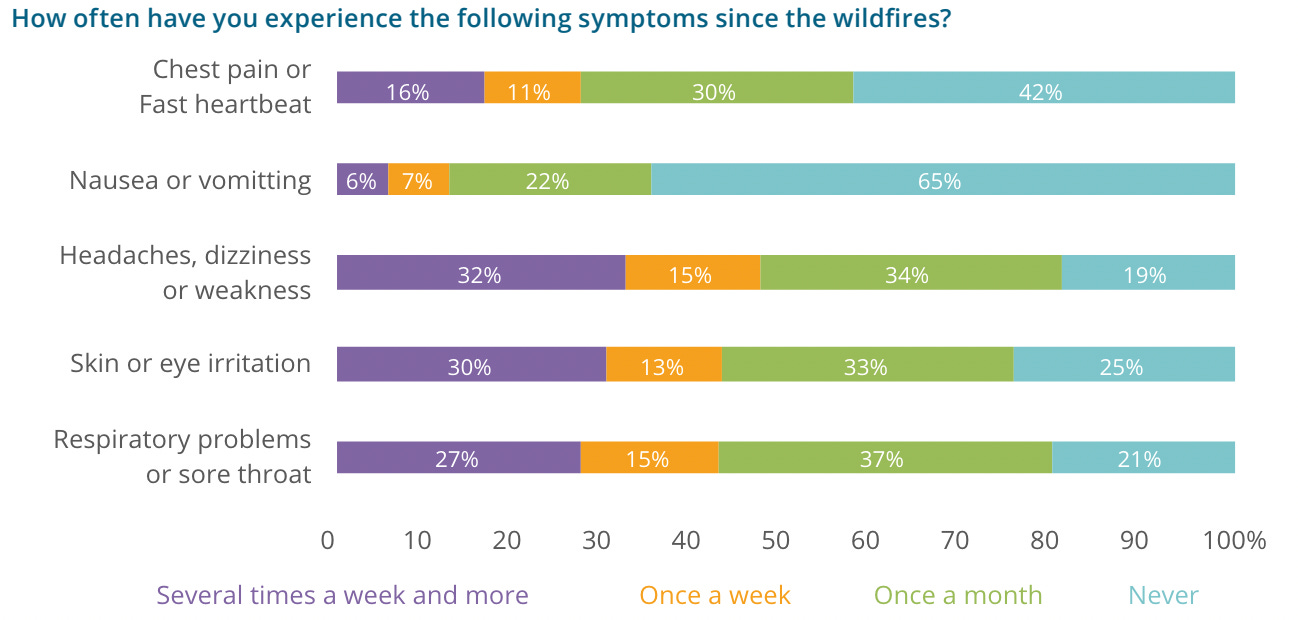
Obesity, high blood sugar, and high blood pressure rates today globally are 50% higher than in 2000—though researchers claim that air pollution still poses a larger threat. Of a study participants in Hawai’i, 75% had respiratory issues, probably from the Maui wildfires last year.
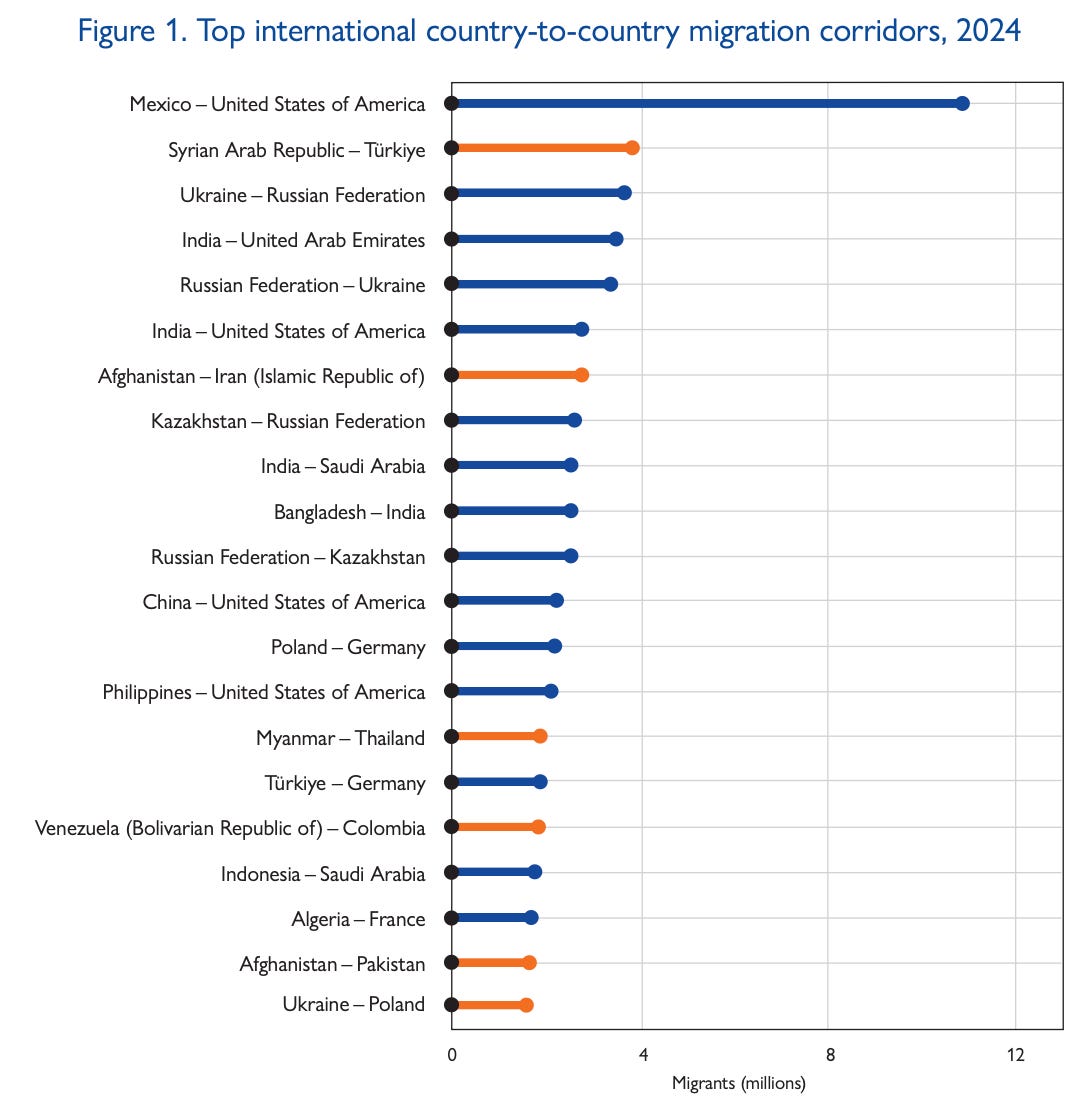
The 2024 World Migration Report is out, and its 384 pages are not as apocalyptic as one might think. However, internally displaced people are at their all-time highest. India, Mexico, Russia, China, and Syria lead the world in emigrants; another document contains the definitions for who exactly constitutes a migrant. Unfortunately much of the data relied upon ends in 2022. Data from this year, not included in the above report, indicates a 40% jump in traffic through the Darien Gap compared to the same time period in 2023.
“The last two years saw major migration and displacement events that have caused great hardship and trauma, as well as loss of life….There have also been large-scale displacements triggered by climate- and weather-related disasters in many parts of the world in 2022 and 2023, including in Pakistan, the Philippines, China, India, Bangladesh, Brazil and Colombia….disinformation tactics are increasingly being used by nefarious actors with negative impacts on public, political and social media discourse on migration….Forced displacement is the highest on record in the modern era…overconsumption and overproduction linked to unsustainable economic growth, resource depletion and biodiversity collapse, as well as ongoing climate change (including global heating) are continuing to grip the world….the risk of further conflict has not been higher in decades, as military spending reached a new record high of USD 2,240 billion in 2022…” -excerpts from the introduction
Another report, focusing on internal displacement, came out last week; its 69 pages show a cross-section of about 47M people displaced by natural disasters (56%) or armed conflict (44%). Most of the disasters were storms & flooding, and most of the conflicts were civil wars of some form. This report also provides detailed region-by-region analyses—with sub-Saharan Africa accounting for 46% of global IDPs.
“Conflict and violence triggered 13.5 million movements, the highest figure for the past 15 years….Disasters and conflict are presented as different triggers, but their impacts can overlap, often leading to repeated and/ or protracted displacement….Drought triggered 331,000 displacements in Somalia….Floods triggered 550,000 displacements in Ethiopia….Conflict and violence triggered 3.8 million displacements in DRC in 2023, a slight fall from the record four million in 2022, but still the second-highest figure globally after Sudan….nearly two-thirds of the internal displacements recorded in 2023 originated from Khartoum state. More than 39 per cent of the state's inhabitants were forced to flee, leaving entire neighbourhoods empty….Criminal and communal violence triggered nearly three-quarters of Nigeria's 291,000 conflict displacements….” -selections from the spotlight on sub-Saharan Africa
Experts are concerned about the mental health impacts that climate change has on our minds. Hotter temperatures reportedly increase depression & aggression. Wildfires and storms can cause PTSD. Workers feel stress and desperation as their usual industries are impacted. And air pollution influences ordinary brain processes in many ways.
Some analysts believe “Peak China” may be over, signaling a period of economic tapering-off, as well as a growing militancy. Increasing U.S. tariffs on Chinese goods are continuing to separate the two economies. The Netherlands finally formed a provisional government, though its proposed immigration & farming policies have set it at odds with the EU.
The Federal Reserve, the U.S. central bank, released a 46-page report on potential climate risks to the banking system’s resilience. As far as I understood, most of the risk lies in extreme weather events and the risk to insurance agencies.
Part of southeast England experienced an outbreak of Cryptosporidium, a diarrhea & vomiting illness, highly contagious, which can last weeks. At least 22 cases have been reported. Meanwhile, the CDC is issuing warnings about the more dangerous strain of monkeypox circulating in the DRC, although cases are currently limited to Africa.
Keep reading with a 7-day free trial
Subscribe to Last Week in Collapse to keep reading this post and get 7 days of free access to the full post archives.